When comparing Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT) and Torque Converter, it’s important to note that they are not the same. Dual Clutch Transmissions and Torque Converters are two distinct types of automatic transmissions used in road cars.
Dual Clutch Transmissions (DCT) and Torque Converters are widely used in automotive applications. They each offer unique features and advantages suitable for different driving conditions and preferences. Understanding the differences between these two transmission systems is essential for making informed decisions when purchasing a vehicle.
Let’s delve deeper into the key characteristics of DCT and Torque Converter to determine which one is better suited for your driving needs.

Credit: topauto.co.za
Contents
What Is Dual Clutch Transmission (dct)?
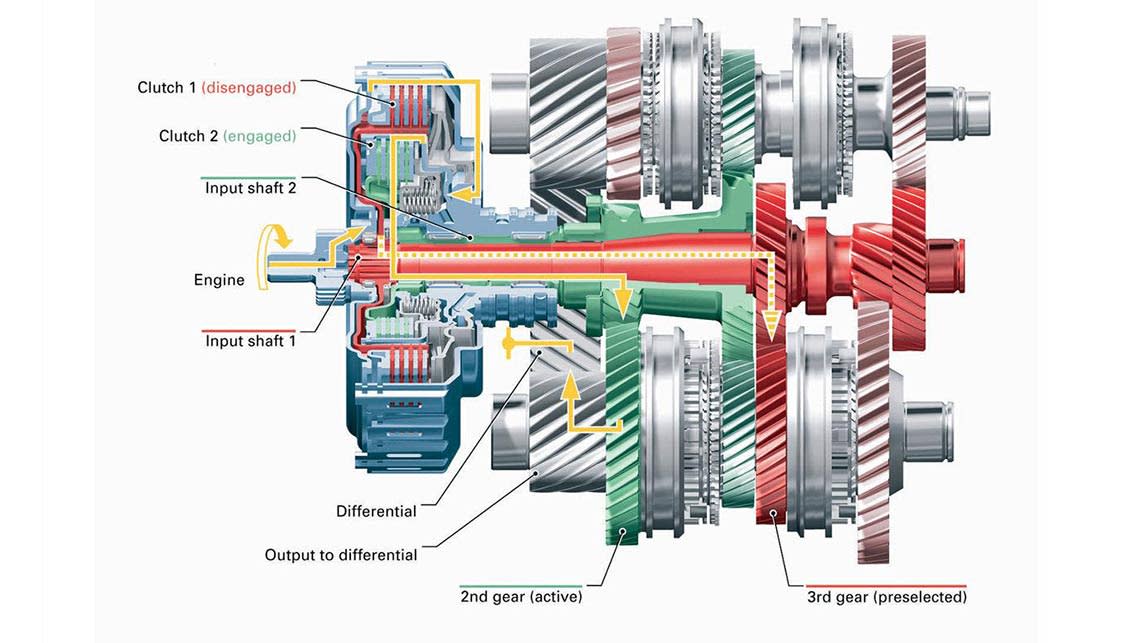
Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT) is a type of automatic transmission that features two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets, allowing for smoother and quicker gear shifts compared to traditional automatic transmissions.
Definition And Design
When looking at the design of a DCT, it employs two separate clutches for the odd and even gear sets. With the ability to pre-select the next gear via the second clutch, it minimizes the power interruption during gear changes, making for a smooth and efficient driving experience.
Advantages
The DCT offers rapid gear changes, resulting in improved acceleration and fuel efficiency. Additionally, the design of the dual clutch transmission allows for seamless power delivery and reduced power loss during gear shifts, enhancing overall driving performance.
Disadvantages
One of the drawbacks of a DCT is its relative complexity, which may lead to higher maintenance and repair costs. Furthermore, the dual-clutch transmission takes up more space under the hood compared to other types of transmissions, potentially impacting vehicle design and layout.
What Is Torque Converter?
In an automatic vehicle, the torque converter plays a vital role in transmitting power from the engine to the transmission. A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling device that functions as a means to transfer rotational power from the engine to the transmission. Let’s delve deeper into its definition, design, advantages, and disadvantages.
Definition And Design
A torque converter is composed of three main elements: the impeller, the turbine, and the stator. It operates by utilizing hydraulic fluid to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. The impeller is connected to the engine, the turbine is connected to the transmission input shaft, and the stator is located between the impeller and turbine to redirect the fluid flow. This design allows the torque converter to smoothly transmit power while providing the ability to multiply torque during acceleration.
Advantages
- Smooth Power Delivery: Torque converters enable smooth and seamless power transmission, providing a comfortable driving experience without noticeable shifting.
- Torque Multiplication: During initial acceleration, torque converters can multiply torque, enabling improved low-end performance.
- Effective at Low Speeds: Torque converters are highly effective at low speeds, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications and stop-and-go driving conditions.
Disadvantages
- Reduced Efficiency: Torque converters can lead to reduced fuel efficiency due to energy losses in the fluid coupling.
- Heat Generation: The fluid friction within the torque converter can generate heat, which may require additional cooling mechanisms.
- Slightly Laggy Response: In some cases, torque converters may exhibit a slight lag in response compared to other transmission systems.
Comparison Between Dual Clutch Transmission And Torque Converter
When it comes to automatic transmissions, Dual Clutch Transmission (DCT) and Torque Converter are two popular options. While both have their advantages and disadvantages, they differ in terms of functionality and operation, performance, efficiency, and suitability for different applications.
Functionality And Operation
DCT operates using two separate clutches, one for odd-numbered gears and the other for even-numbered gears. This allows for rapid and seamless gear shifts, providing a smooth driving experience. On the other hand, Torque Converter uses a fluid coupling to transmit power from the engine to the transmission, resulting in a smoother and more gradual engagement of gears.
Performance
DCT is known for its exceptional performance, especially in high-performance vehicles. The dual clutches allow for quick and precise gear changes, offering faster acceleration and improved overall performance. Torque Converter, on the other hand, provides smoother and more gradual acceleration, making it suitable for applications that involve heavy loads.
Efficiency
In terms of efficiency, DCT generally offers better fuel economy compared to Torque Converter. The rapid and seamless gear shifts of DCT minimize power loss and maximize engine efficiency. On the other hand, Torque Converter transmissions are generally less efficient, but they offer increased torque at low revs.
Suitability For Different Applications
DCT is often preferred in sports cars and high-performance vehicles due to its fast and precise gear changes. Its ability to deliver quick acceleration and responsive driving makes it ideal for those looking for a thrilling driving experience. Torque Converter, on the other hand, is commonly found in larger vehicles and those that require towing capabilities. Its ability to provide high torque at low revs makes it well-suited for applications that involve heavy loads.
In conclusion, while both DCT and Torque Converter have their own strengths and weaknesses, the choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific needs and preferences of the driver. Whether it’s high performance or towing capability, understanding the functionality, performance, efficiency, and suitability of each transmission can help make an informed decision.

Credit: www.autodeal.com.ph

Credit: www.dubizzle.com
Conclusion
When comparing dual clutch transmission (DCT) and torque converter, it is evident that they are not the same. DCT offers quick and seamless gear changes, making it ideal for high-performance applications. On the other hand, torque converters excel in heavy load situations.
Both have their advantages and disadvantages, with DCTs taking up more space under the hood. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on individual needs and preferences. Understanding the differences will help you make an informed decision for your vehicle.